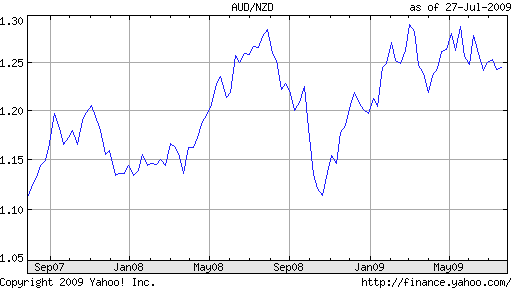
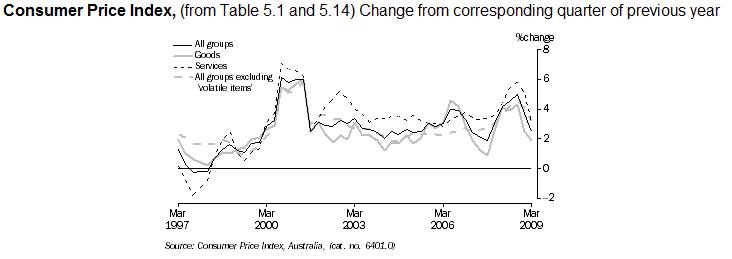
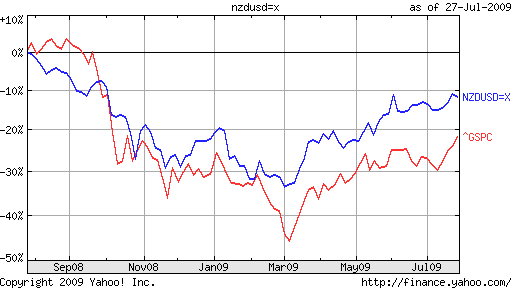
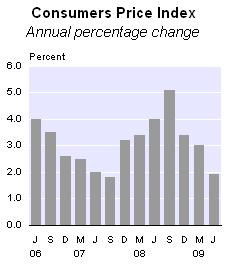
The basis for why several of the traders lose and do not attain currency trading success is regularly attributed to a lack of discipline, though this is not the main cause, it’s just a small part of the trouble.
The main cause is a short of “strong concentration”, this indeed should be looked in to as the majority of traders are ignorant of it.
If you desire to attain currency trading success you require “strong concentration” and this denotes concentrating on how and why forex markets actually function and what you have to do to eventually succeed. The majority of traders just will not follow this and they will lose.
Do your work smartly; don’t make things harder for yourself:
In several industries to attain success the more you place in the more you get out in terms of returns; this is not right in currency trading.
What you require to study is that to attain real good success in currency trading you will have to be working real smart, you must not be playing tough rather you must be applying an easy system that should have you spend less time and better profit.
You can make a better currency trading process in just an hour a day and create triple digit annual gains! Simplicity is the main thing to attain currency trading success.
Trade with likelihood:
These days, there is a massive industry that informs us of analytical theories and functions and you can choose market bottoms and tops with technical correctness.
The other huge fairy tale is day trading.
You can attempt to trade pretty harder as you desire, but the odds are not in your goodwill in day trading, as you will not have sufficient profits to wrap your predictable losses.
You require to trade better in the longer run and this is where the likelihood of success is more and this is one of the single method with which you will land up with success in currency trading.